
|
 Home Home
 Projects Projects
 Experiments Experiments
 Circuits Circuits
 Theory Theory
 BLOG BLOG
 PIC Tutorials PIC Tutorials
 Time for Science Time for Science
|
| ||
|
14 December 2009 Author: Giorgos Lazaridis Low Cost PIC ThermometerThere are certain citations where we need to measure the temperature to one or more places/positions, but it is not required high accuracy. I for example, needed once to measure (and monitor) the temperature to 6 hard disc drives and 2 more positions in a PC box. Totally i needed 8 temperature sensors. High accuracy temperature sensors cost 2 or more Euro. Only for the sensors i would need more than 16 Euro. Instead, i used simple thermistors, for 0.25 Euro each. The total price for 8 thermistors was 2 Euro. This is the most important reason why someone would prefer to use a thermistor instead of t sophisticated temperature sensor. There is a major drawback though. Cheap thermistors have lower accuracy. I am not talking about 4 and 5oC. The once i used had about 2oC in temperatures much higher than 25 degrees. For room temperatures, the accuracy was very satisfying, and sometimes the measurement of the thermistor was the same with the accurate temperature meter. The inaccuracy comes basically from the characteristic of each thermistor. The characteristic is a line that shows how the resistance of the thermistor is changed according to the temperature change. Over the years, thermistors with almost linear characteristic line have been made. But still it is not exactly linear. This means that a simple formula solution for a straight line, will produce in some cases wrong results. The circuit in operationThe theory of operation I will use the thermistor from this experiment. I tried to re-generate the characteristic line of this thermistor. The experiment was not scientific though. For a scientific experiment, i would need a controlled environment with expensive equipment. With the equipment that i can afford, i had some very good results though. For temperatures from -9oC up to 45oC, this thermistor had an almost linear characteristic. Using the least squares method, i found the line slope and offset:
b = 62.07 The above numbers comes from a 1K thermistor connected with a 1K 1% metal film resistor as a voltage divider. I will use the same connection here to have the same results. Using the PIC's built-in analog to digital converter, i will measure the output voltage of the voltage divider. Directly, i can calculate the temperature using the formula for the straight line: Y = a*X + b solving for X:
The Circuit I use the 16F1937 PIC microcontroller for this project. Any other PIC with a built-in ADC module will work the same. There is no special reason why i used this 40-pin PIC for such a small circuit. I just have always one connected to a breadboard and i used is for saving time. It is important to use a metal film resistor with 1% or better accuracy. A carbon 5% resistor has a very high reading error. I tried it and was disappointing. The LED is blinking every time a new measurement is taken. Here is the schematic diagram of the circuit: 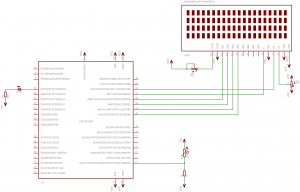
The thermistor is a NTC thermistor. If you use a PTC thermistor, then you need to switch places between the metal film resistor and the thermistor. Downloads Here are all the files needed as well as the full assembly listing, to re-compile the program:
For those that do not want to recompile and wants it as-is, here is the compiled hex version to directly upload to the PIC:
Bill Of Materials Relative pages Comments
|
|
 Contact Contact
 Forum Forum
 Projects Projects
 Experiments Experiments
 Circuits Circuits
 Theory Theory
 BLOG BLOG
 PIC Tutorials PIC Tutorials
 Time for Science Time for Science
 RSS RSS
Site design: Giorgos Lazaridis © Copyright 2008 Please read the Terms of services and the Privacy policy |